Ontario’s Neuroscience Data Opportunity
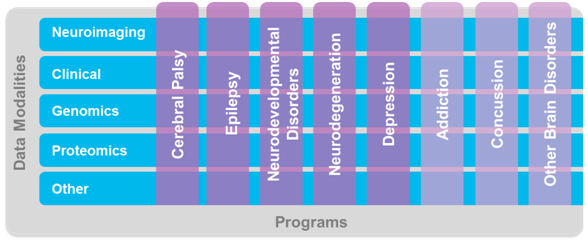
The Ontario Brain Institute is a provincially‐funded, not‐for‐profit research centre seeking to maximize the impact of neuroscience and establish Ontario as a world leader in brain research, commercialization and care. Convergent partnerships are created between researchers, clinicians, industry, patients, and their advocates to foster discovery and deliver innovative products and services that improve the lives of those living with brain disorders. To help realize this goal, the OBI funds Integrated Discovery Programs (ID Programs) spanning the areas of epilepsy, cerebral palsy, neurodegenerative disorders, depression, concussion, neurodevelopmental disorders and others. The creation of these programs has resulted in a real data opportunity. Integrating and sharing the wealth of Ontario-based brain research data has immense potential to inspire innovative, impactful diagnostics and treatments for brain disorders. To facilitate collaboration and discovery, OBI has developed Brain-CODE. Brain-CODE is an extensible informatics platform that manages the acquisition, storage and sharing of multidimensional data collected from patients with a variety of brain disorders (Figure 1). As an ID program researcher, Brain-CODE is your data storage solution, analytics toolbox, and collaboration hub. Your commitment to data sharing will transform Brain-CODE into a platform for discovery.
By collecting data elements across diseases in a standardized manner this complex matrix arises: not only can deep comparisons across data modalities be made within one single brain disorder, but so too can deep comparisons begin to be investigated across brain disorders. Brain-CODE aims to facilitate data-driven discovery in neuroscience unlike ever before.
Brain-CODE for Everyone
Brain-CODE is not just for OBI funded studies, other research teams can benefit from Brain-CODE. Please contact help@braincode.ca for more information on how to host your neuroscience data on Brain-CODE to facilitate long term storage, analysis, sharing, and collaboration.
Brain-CODE's Guiding Principles
1) Privacy & Security
Brain-CODE adheres to high levels of data privacy and security. Encryption and de-identification tools are used to protect participant data. Brain-CODE is developed in accordance with Privacy-by-Design principles.
2) Open & Collaborative
Brain-CODE was designed to enable data sharing and to foster collaborations among a broader researcher community. Allowing researchers to make their data open to other researchers studying the same or different disorders is becoming a common approach that leads to ground-breaking discoveries.
3) Interdisciplinary & Integrated
Brain-CODE facilitates data sharing within and across brain disorders to further understand mechanisms of disease, commonalities, comorbidities, while promoting novel hypothesis generation. This integrated approach to research sparks collaboration between clinicians, researchers, basic scientists, industry partners, participants and patient advocacy groups.
4) Patient Centred
The fundamental purpose of data sharing and collaboration on Brain-CODE is to enable greater insights into the data and ultimately drive faster translation of the discoveries towards positive patient outcomes.
5) Standardization
Standardization is a high priority for Brain-CODE and it ensures interoperability of datasets. Standardization efforts including clinical common data elements (CDEs), MEG and EEG standardization forms, and fBIRN phantom scans, help to define and format the vast array of clinical, neuroimaging and molecular data to optimize downstream integrative analyses.
6) Discovery for Health Impact
By facilitating collaboration on a platform of standardized neuroscience data, the stage is set for integrative big data analytics. Integration of datasets across disciplines has the potential to catalyze new discoveries which can be translated into new diagnostics and treatments for brain disorders.
At the Heart of Brain-CODE
Brain-CODE is developed by experts in research informatics
OBI has contracted Indoc Systems to support the design and implementation of the platform and research operational services.
Hardware
Brain-CODE is hosted on secure computing infrastructure located in Canada. As the use and requirements for Brain-CODE grow, additional computing nodes can be allocated for increased data storage, specialized data processing, added demand for federation, and intensive concurrent analytical tasks.
Software
The Brain-CODE neuroinformatics platform is designed around five key components: data capture, data storage, data integration, analytics, and federation. Electronic data capture software enables researchers to enter and store multi-modal data on one convenient web-based interface. REDCap for clinical data, LabKey for molecular and genomics data, and SPReD (based upon XNAT) for imaging data, have been integrated within Brain-CODE to suit diverse research needs.
Integration of the diverse data sets is facilitated by a middleware application and standardized data infrastructure. An internal data federation server enables the heterogeneous sets of research data to be regrouped and organized for downstream access and use.
Brain-CODE also implements a privacy preserving record linking procotol to link participant data with other national and international health databases.
Computing Workspaces
Computing workspaces are available to registered Brain-CODE users to perform data processing and analysis using tools such as Python, R, etc. Researchers may also bring their own software licenses into the workspace environment to benefit from tools they are more familiar with.